소개
torchvision.datasets.CocoDetection은 PyTorch에서 MS COCO 데이터셋을 기반으로 Object Detection Task 모델 개발을 위한 Dataset 클래스임.
다음의 상속 관계를 가짐:
torch.utils.data.Dataset
↑
torchvision.datasets.vision.VisionDataset
↑
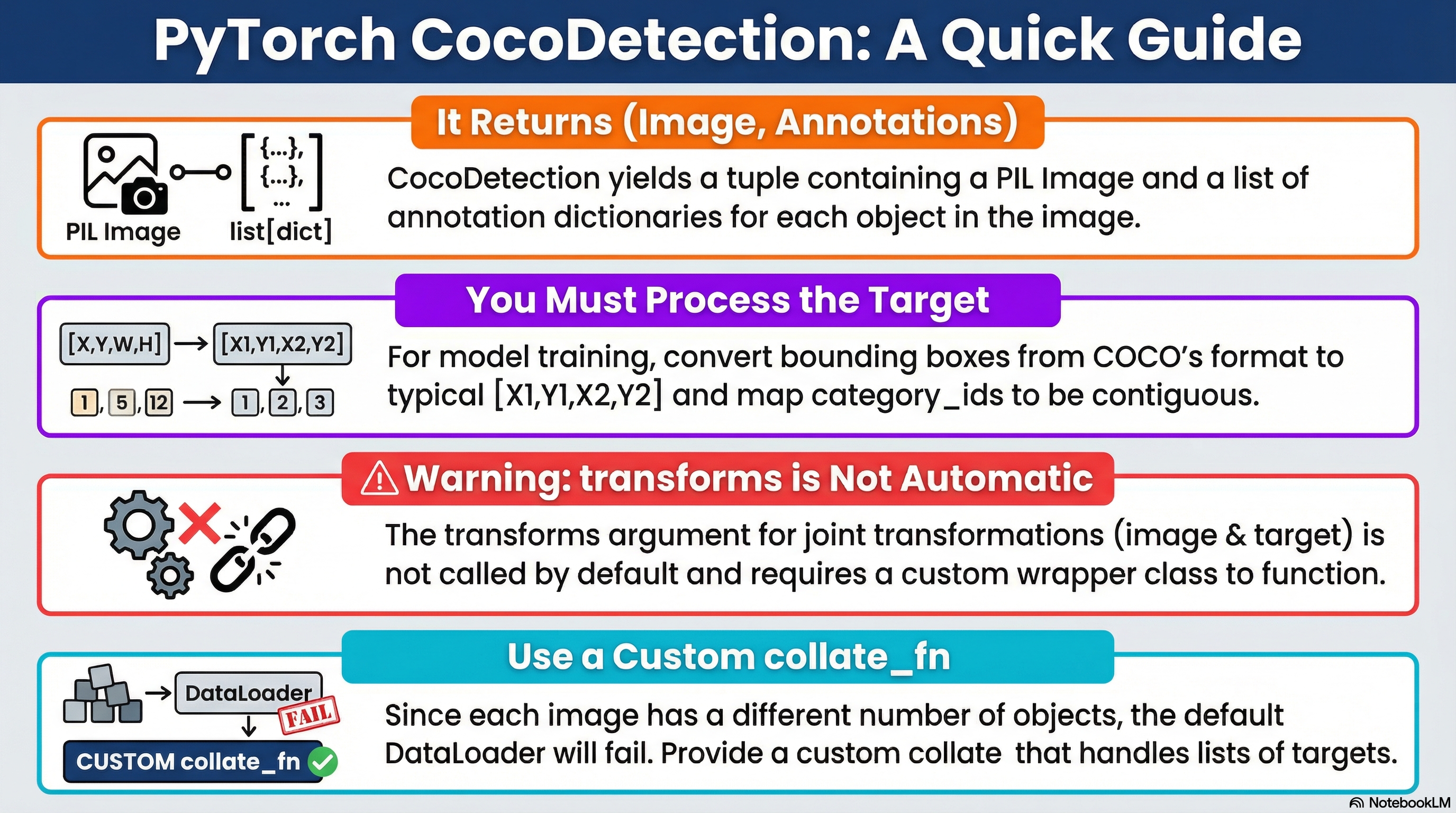
torchvision.datasets.CocoDetectionDataset:__len__,__getitem__메서드를 제공 (=DataLoader에서 동작되도록)VisionDataset:transform,target_transform,transforms같은 변환 등의 전처리를 정의.CocoDetection: COCO 의 디렉토리 및 JSON 을 읽어서(image, target)을 만드는 COCO 전용 로더.
주의할 점은
VisionDataset은 transforms를 “정의”는 하지만, 자동 호출을 보장하지 않음.CocoDetection은 기본적으로transform(image-only) /target_transform(target-only) 패턴으로 동작CocoDetection는 내부에서transforms(image, target)를 자동 호출하지 않음: composit input에 대한 v2기능을 사용하려면 wrapper 필요.
original API documentation:
https://docs.pytorch.org/vision/main/generated/torchvision.datasets.CocoDetection.html
CocoDetection — Torchvision main documentation
Shortcuts
docs.pytorch.org
관련 gist: https://gist.github.com/dsaint31x/56feffe9b8c7f039e24ec429ebe089ab
dl_COCO_Detection_Simple_Example.ipynb
dl_COCO_Detection_Simple_Example.ipynb. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
gist.github.com
Signature
class torchvision.datasets.CocoDetection(
root: str,
annFile: str,
transform: Optional[Callable] = None,
target_transform: Optional[Callable] = None,
transforms: Optional[Callable] = None
)인자 설명
- root (str 또는 pathlib.Path):
- COCO 이미지들이 저장된 이미지 루트 디렉토리
- 예:
coco/val2017/
- annFile (str):
- COCO annotation JSON 파일 경로
- 예:
coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json
- transform (callable, optional):
- 이미지(PIL) 에 적용할 변환 함수
- target_transform (callable, optional):
- target(어노테이션) 에 적용할 변환 함수
- geometric transform을 적용할 수 없다는 단점 가짐.
- transforms (callable, optional):
(image, target)을 함께 받아 변환하는 함수(= joint transform 슬롯)를 넘겨받는 파라미터- v2 의 composit input에 대한 처리용이나 실제로는 지원되지 않음.
- 즉, CocoDetection은 이를 getitem에서 호출하지 않으므로 기본 구현만으로는 적용되지 않음.
참고:
CocoDetection은
내부적으로pycocotools가 필요함.
반환값(= classification과 가장 큰 차이점을 보임)
__getitem__(index)는 다음을 반환:
- image: PIL Image
- target: 해당 이미지의 annotation들이 들어있는
list[dict]- 각 dict에 보통
bbox(COCO는 XYWH),category_id,segmentation,iscrowd등이 포함
- 각 dict에 보통
CocoDetection은ImageFolder처럼 (image, class_index) 를 주는 “분류용” 데이터셋이 아니라,
(image, 객체별 annotation 리스트) 를 주는 Detection 용 데이터셋임.
CocoDetection의 주요 속성
주요 attributes
meta information
- coco
pycocotools.coco.COCO객체- annotation JSON 전체를 파싱한 결과
- category, image, annotation 조회의 중심 API
- ids
- 데이터셋에 포함된 COCO image_id 리스트
__len__()은 이 리스트의 길이를 반환__getitem__(idx)에서image_id = ids[idx]방식으로 사용됨
- categories (간접적)
self.coco.loadCats(self.coco.getCatIds())로 접근 가능- ImageFolder처럼
classes리스트를 직접 멤버로 들고 있지는 않음
참고로 classes / class_to_idx 없음
data 관련
참고로 ImageFolder의 imgs / samples 이 없다는 점을 기억할 것
- annotation (내부적으로 coco가 관리)
- annotation은
self.coco내부 구조로 관리됨 __getitem__에서 특정image_id에 해당하는 annotation들을list[dict]형태의 target으로 구성함
- annotation은
- targets (명시적 리스트 없음)
- 모든 샘플의 타겟을 미리 리스트로 저장하지 않음
- 각
__getitem__호출 시 on-the-fly로 생성됨
Loading 관련
- root
- 이미지 파일들이 저장된 디렉토리 경로
file_name과 결합하여 실제 이미지 경로 생성
- 이미지 로딩 방식 (
loader속성 없음)- ImageFolder와 달리
loader속성을 노출하지 않음 - 내부적으로
PIL.Image.open(path).convert("RGB")사용 - Tensor로 바로 로드하려면
transform또는 wrapper에서 처리
- ImageFolder와 달리
Transform 관련
- transform
- image에만 적용되는 변환
- 기본 입력: PIL Image
- 출력: PIL Image 또는 Tensor (사용자 정의)
- target_transform
- target에만 적용되는 변환
- target은
list[dict]구조 - 주 용도:
- Coco의 불연속적인
category_id를 contiguous label로 매핑 dtype변경- 필드 추가/제거 에도 사용가능.
- Coco의 불연속적인
- 절대로 image에 의존하는 geometric transform을 수행 등에는 부적합하다는 점을 기억할 것.
- transforms (joint transform 슬롯)
(image, target)를 함께 처리하기 위한 슬롯- VisionDataset에 정의만 되어 있으며
- CocoDetection에서는
__getitem__에서 호출되지 않음 - detection/segmentation에서 사용하려면 wrapper 또는 상속으로 직접 호출해야 함
methods
__len__()- 전체 sample(= 이미지)의 개수를 반환
- 내부적으로는 COCO의 이미지 id 리스트(
self.ids) 길이를 반환하는 형태
__add__()- 구현이 제대로 안되어 있음.
- 대신
torch.utils.data.ConcatDataset([ds1, ds2])를 사용
__getitem__(idx)dataset[idx]호출 시 실행되며 다음의 과정으로 동작.image_id결정image_id = self.ids[idx]ImageFolder처럼self.samples[idx]에서 path를 꺼내는 구조랑 차이가 있음.
- 해당
image_id의 annotation 로드- COCO API로
image_id에 해당하는 annotation id들을 얻고, - 이를 로드하여
target = list[dict]로 구성 - 각 dict는 bbox, category_id, segmentation, iscrowd, area 등 포함
- COCO API로
- 이미지 파일 경로 계산 후 로드
img_info = coco.loadImgs(image_id)[0]에서file_name을 얻고,path = os.path.join(root, file_name)로path를 얻고image = PIL.Image.open(path).convert("RGB")형태로 로드
transform/target_transform적용transform이 있으면:image = self.transform(image)target_transform이 있으면:target = self.target_transform(target)
(image, target)반환
- 최종 반환:
- `image: 기본은 PIL Image (transform에 따라 Tensor 등으로 바뀔 수 있음)
target: 기본은list[dict]v2 transforms / composite input관련
- 다시한번 말하지만,
CocoDetection은 기본적으로transforms(joint: (image, target))를__getitem__에서 호출하지 않는 구현임.- v2의 composite input(예:
boxes/masks/keypoints를image와 함께 변환) 파이프라인을 쓰려면 - wrapper 또는 상속으로
__getitem__에서 직접(image, target)을 joint transform 에 인자로 넘기는 구현 필요.
- v2의 composite input(예:
- 같은 맥락에서 v2에서 기하 변환(Resize/Flip 등)과 함께
boxes/masks/keypoints를 정확히 따라가게 하려면,target을tv_tensors.BoundingBoxes,tv_tensors.Mask등으로 구성하고image도v2.ToImage()등으로 tv_tensor Image 로 변환 후(image, target)형태로 joint transform을 호출하는 패턴을__getitem__에 구현해야 함.
정리하면
- target을
tv_tensors.BoundingBoxes,Mask,Keypoints등으로 구성 target_transform으로 처리하면 안됨.torchvision.transforms.v2의trasnforms를 통한 joint transform으로 처리가 권장되나 wrapper로 구현해야 한다.
Detection 을 위한 COCO 디렉토리 구조
coco/
├─ train2017/
├─ val2017/
└─ annotations/
├─ instances_train2017.json
└─ instances_val2017.json- CocoDetection에서 필요한 건
instances_*.json임.
CocoDetection 기본 사용법
from torchvision.datasets import CocoDetection
IMG_ROOT = "coco/val2017"
ANN_FILE = "coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
ds_raw = CocoDetection(root=IMG_ROOT, annFile=ANN_FILE)
img, target = ds_raw[0]
print(type(img)) # PIL.Image.Image
print(type(target)) # list
print(len(target)) # object 개수
print(target[0].keys()) # bbox, category_id, segmentation, iscrowd, ...
print(target[0]["bbox"])# [x, y, w, h] (COCO: XYWH)target 은 다음의 특징을 가짐:
target은list[dict](한 이미지 안의 객체가 N개면dict가 N개)bbox는XYWH임: torchvision에선"boxes"라고 지칭하며XYXY형태임.- category는
category_id(COCO id) : 문제는 contiguous 하지 않음 (contiguous하게 바꿔야 모델 훈련에 편함.) segmentation은 polygon/RLE가 섞여 있을 수 있음.iscrowd는 evaluation/segmentation 에서 중요한 의미가 있음 (예를 들어 판정등에서iscrowd=1은 무시)
Detection 모델이 원하는 형태로 반환값의 target 변환하기
torchvision detection 모델(Faster R-CNN 등)은 보통 다음을 기대함.:
target = {
"boxes": FloatTensor[N,4] # XYXY
"labels": LongTensor[N]
# (옵션) image_id, area, iscrowd ...
}COCO의 target에는 다음이 포함될 수 있음:
bbox(XYWH)segmentation(polygon 또는 RLE)keypoints
XYXY로 변환
COCO의 bbox=[x,y,w,h] 를 XYXY 로 변환하는 경우 많음.
import torch
def coco_list_to_det_target(ann_list, image_id=None):
boxes = []
labels = []
iscrowd = []
area = []
for obj in ann_list:
x, y, w, h = obj["bbox"]
boxes.append([x, y, x + w, y + h]) # XYWH -> XYXY
labels.append(obj["category_id"])
iscrowd.append(obj.get("iscrowd", 0))
area.append(obj.get("area", w * h))
if len(boxes) == 0: # 객체가 없는 경우 처리.
boxes_t = torch.zeros((0, 4), dtype=torch.float32)
labels_t = torch.zeros((0,), dtype=torch.int64)
iscrowd_t = torch.zeros((0,), dtype=torch.int64)
area_t = torch.zeros((0,), dtype=torch.float32)
else:
boxes_t = torch.tensor(boxes, dtype=torch.float32)
labels_t = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.int64)
iscrowd_t = torch.tensor(iscrowd, dtype=torch.int64)
area_t = torch.tensor(area, dtype=torch.float32)
target = {
"boxes": boxes_t,
"labels": labels_t,
"iscrowd": iscrowd_t,
"area": area_t,
}
if image_id is not None:
target["image_id"] = torch.tensor([image_id], dtype=torch.int64)
return targetcategory_id 를 contiguous label 로 매핑
COCO의 category_id(예: 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, …)는 contiguous가 아님. 80개이나 ID는 그 이상으로 할당됨. 즉 비는 번호 존재.
문제는 torchvision detection 모델 학습에는 보통 labels를 1..K (0은 background) 로 맞추는 경우가 많다는 점임.
그래서
- 학습 시:
category_id를contiguous_id로 바꾸고 - 평가/
COCOeval시:contiguous_id를 다시category_id로 되돌리는 방식이 많이 사용됨.
import torch
# mapping용 dict 생성.
def build_coco_category_mapping(coco_api):
"""
coco_api: pycocotools.coco.COCO 객체 (coco_gt)
return:
catid_to_contig: {category_id -> contiguous_id(1..K)}
contig_to_catid: {contiguous_id(1..K) -> category_id}
"""
cat_ids = coco_api.getCatIds() # COCO category ids
cat_ids = sorted(cat_ids)
catid_to_contig = {cat_id: i + 1 for i, cat_id in enumerate(cat_ids)}
contig_to_catid = {i + 1: cat_id for i, cat_id in enumerate(cat_ids)}
return catid_to_contig, contig_to_catid
# dict-target용 transform (앞서 다룬 XYXY변환 포함)
def make_target_transform_catid_to_contig(catid_to_contig):
"""
catid_to_contig: dict {category_id -> contiguous_id}
returns: callable(target_dict) -> target_dict
"""
def _tf(target):
image_id = ann_list[0]["image_id"] if len(ann_list) > 0 else None
# 1) 기존 함수 그대로
target = coco_list_to_det_target(ann_list, image_id=image_id)
# 2) labels만 contiguous로 변환
# target["labels"]는 COCO category_id 텐서라고 가정
labels = target["labels"]
if labels.numel() == 0:
return target
# 파이썬 dict 매핑 (labels가 크지 않아서 보통 충분)
mapped = [catid_to_contig[int(x)] for x in labels.tolist()]
target["labels"] = torch.tensor(mapped, dtype=torch.int64)
return target
return _tf
# 사용하는 코드
coco_gt = COCO(ANN_FILE)
catid_to_contig, contig_to_catid = build_coco_category_mapping(coco_gt)
target_transform = make_target_transform_xyxy_and_catid_to_contig(catid_to_contig)
ds = CocoDetection(
root=IMG_ROOT,
annFile=ANN_FILE,
transform=img_transform,
target_transform=target_transform,
)transforms 구현
앞서 애기한 transforms를 처리하는 변경은 기하학적 변환을 image와 bbox, mask 등에 똑같이 적용하기 위해 필요하나 이는 Wrapper나 상속으로 구현해야 하는 부분임.
기본으로 제공하는 CocoDetection만을 사용하는 경우 가급적 geometric transform 을 이용하는 data aug.를 위한 transform은 사용하지 않는게 좋음.
제대로 처리한 wrapper의 구현은 다음 gist를 참고:
https://gist.github.com/dsaint31x/56feffe9b8c7f039e24ec429ebe089ab
dl_COCO_Detection_Simple_Example.ipynb
dl_COCO_Detection_Simple_Example.ipynb. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
gist.github.com
CocoDetection을 사용할 경우, DataLoader에서 collate_fn 을 지정해야 함.
객체 수가 이미지마다 다르므로 torch.stack기반의 default_collate는 동작하지 않음.
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
def collate_fn(batch):
images, targets = zip(*batch)
return list(images), list(targets)
Example
v2 transforms 를 통한 composite input에 대한 joint transform 이 안되므로 기하학적 변환은 사용을 피해야함.
이를 사용하려면, Wrapper 를 통해 transforms에 대한 다음의 기능 구현들이 필요함.
- v2의
tv_tensor의 텐서로 변환. transforms를 joint transform을 제대로 하도록XYWH를XYXY형태로.
다음의 예는 이를 제외한 간단한 사용법임.
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from torchvision.datasets import CocoDetection
from torchvision.transforms import v2
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch
IMG_ROOT = "coco/val2017"
ANN_FILE = "coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
# 1) mapping + target_transform 준비 (이전에 설명한 함수들임)
coco_gt = COCO(ANN_FILE)
catid_to_contig, contig_to_catid = build_coco_category_mapping(coco_gt)
target_tf = make_target_transform_xyxy_and_catid_to_contig(catid_to_contig)
# 2) 이미지 transform (기하학적 변환 사용금지)
img_only = v2.Compose([
v2.ToImage(),
v2.ToDtype(torch.float32, scale=True),
])
# 3) CocoDetection만 사용: transform=이미지, target_transform=타겟
ds = CocoDetection(
root=IMG_ROOT,
annFile=ANN_FILE,
transform=img_only,
target_transform=target_tf,
)
loader = DataLoader(ds, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
images, targets = next(iter(loader))
print(images[0].dtype, images[0].shape)
print(targets[0].keys(), targets[0]["boxes"].shape)
print("labels example:", targets[0]["labels"][:10])같이보면 좋은 자료들
2025.12.16 - [ML] - MS COCO (Microsoft의 Common Object in Context) Dataset
MS COCO (Microsoft의 Common Object in Context) Dataset
COCO 데이터셋은 여러 종류의 task 에 대한 모델을 훈련시킬 수 있음: 다음의 task들로 구분됨.1. Object Detection (객체 탐지)목적: 이미지 안에 있는 객체의 location 과 class (=category)를 추출 : things만annotat
ds31x.tistory.com
2025.12.16 - [ML] - pycocotools COCO API 기초
pycocotools COCO API 기초
pycocotools COCO API에서 자주 쓰는 메서드들에 대한 정리:getAnnIdsgetCatIdsgetImgIdsloadAnnsloadCatsloadImgsloadResshowAnns2025.12.16 - [ML] - MS COCO (Microsoft의 Common Object in Context) Dataset MS COCO (Microsoft의 Common Object in Cont
ds31x.tistory.com
'ML' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAX (Just After eXecution)소개 (0) | 2026.01.16 |
|---|---|
| Deployment 가능한 HF Custom (Vision) Model 만들기 (0) | 2025.12.18 |
| Object Detection 태스크에 대한 모델 평가를 COCO API로 하기 (0) | 2025.12.16 |
| pycocotools COCO API 기초 (0) | 2025.12.16 |
| MS COCO (Microsoft의 Common Object in Context) Dataset (1) | 2025.12.16 |



