1. Axes3D
3D plot 을 수행하는 주요 Class 는 Axes3D 임: mpl_toolkits.mplot3d 모듈
이전 버전에서 사용하던 방식.
# option 1 : Matplotlib 1.0.0 이전의 방식.
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4,4), dpi=100)
ax = Axes3D(fig)
print(type(ax))- 개인적으로는 이 방식보다 아래의 방식을 선호함.
fig에 3D를 위한 Axes객체를 추가하는 방식.
# option 2
# 3.2.0 버전 이후로는 굳이 Axes3D등을 import 할 필요 없음.
# 각 subplot에 따로 따로 3D를 적용할 때 이용됨.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4,4), dpi=100)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
print(type(ax))- option 2: mix axes objects with 2D and 3D projections within the same figure.
fig의 모든 Axes가 3D로 설정되는 방식.
# option 3
#
# fig 내의 모든 Axes객체에 3D적용.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(4,4),
subplot_kw = {'projection': '3d'})
print(type(ax))- option 3: apply the same
subplot_kwoption to all the subplots added to a figure.
2. 3-D Plots
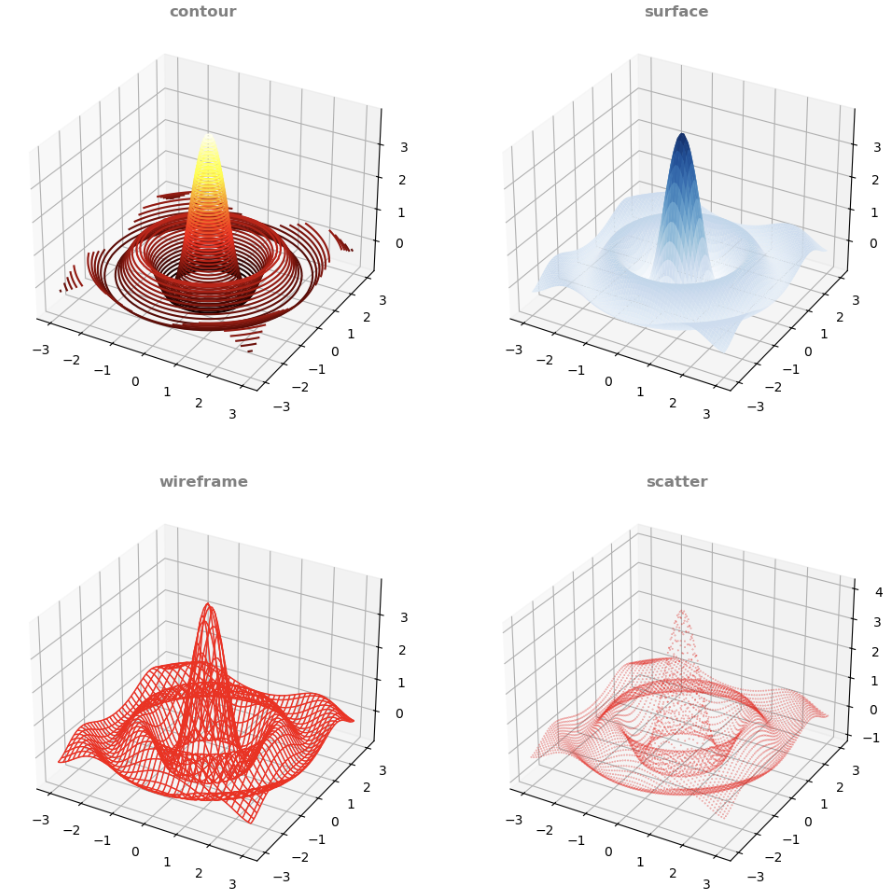
Axes3D 에서 제공하는 3D plot 중 많이 사용되는 것들은 다음과 같음.
plot_surface: 가장 많이 사용되는 방식. contour와 함께 그려지기도 함.plot_wireframe: surface와 함께 가장 많이 사용되는 방식 중 하나임.contour( orcontourf) : 입체감은 떨어지는 편이며 filling이 수행되는 contourf가 단독으로는 보다 나음.
이외에도 scatter도 많이 사용됨.
다음 그림을 참고.
2-1. Parameters
이들은 meshgrid를 통해 얻은 x 좌표 matrix, y좌표 matrix와
독립변수들에 결정된 z값 matrix 가
positional arguments로 할당하는게 일반적임.
rstride,cstride- row and column stride 로 데이터에서 어느정도를 graph를 그리는데 사용할지를 정함.
cmap- color map을 지정. e.g.:
mpl.cm.Blues
- color map을 지정. e.g.:
antialiased- 보다 부드럽게 보이는 antialiased 기능을 켤지 여부,
TrueorFalse
- 보다 부드럽게 보이는 antialiased 기능을 켤지 여부,
다음의 예제는 앞서 4가지 plot을 그려줌: 사실 모든 axes객체에 3D를 적용하는 경우엔 아래 코드가 비효율적임.
연습을 위해 단순 반복을 함수로 만들지 않은 경우임.
import matplotlib as mpl
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,12), dpi=100)
ax0 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,1, projection='3d')
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,2, projection='3d')
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,3, projection='3d')
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,4, projection='3d')
# -----------------------------------
xs = ys = np.linspace(-3, 3, 74)
x, y = np.meshgrid(xs, ys)
R = np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
z = np.sin(4 * R) / R
# -----------------------------------
ax0.set_title('contour', fontdict={'fontsize':'large',
'color':'gray',
'fontweight':'bold'})
p0 = ax0.contour(x,y,z,
# zdir='z',
# offset=0,
levels = 50,
cmap=mpl.cm.hot)
# -----------------------------------
ax1.set_title('surface', fontdict={'fontsize':'large',
'color':'gray',
'fontweight':'bold'})
p1 = ax1.plot_surface(x,y,z,
rstride=1, cstride=1,
linewidth=1,
antialiased=True,
cmap=mpl.cm.Blues)
# -----------------------------------
ax2.set_title('wireframe', fontdict={'fontsize':'large',
'color':'gray',
'fontweight':'bold'})
p2 = ax2.plot_wireframe(x,y,z,
rstride=2, cstride=2,
linewidth=1,
color='red')
# -----------------------------------
ax3.set_title('scatter', fontdict={'fontsize':'large',
'color':'gray',
'fontweight':'bold'})
p3 = ax3.scatter(x,y,z,
s=.1, alpha=0.5,
color='red')
plt.show()3. View Point 설정.
Axes3D 객체에서 그린 graph를 보는 시점은 view_init 메서드로 설정함 (degree로 설정).
elevation: 첫번째 parameterazimuth: 두번째 parameter
ax.view_init(80, 0)
다음의 코드는 위 동영상을 위한 코드임.
from matplotlib import animation
import matplotlib as mpl
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(3,3), dpi=50)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
xs = ys = np.linspace(-3, 3, 74)
x, y = np.meshgrid(xs, ys)
R = np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
z = np.sin(4 * R) / R
ax.set_title('contour', fontdict={'fontsize':'large',
'color':'gray',
'fontweight':'bold'})
def init():
p = ax.contour(x,y,z,
# zdir='z',
# offset=0,
levels = 50,
cmap=mpl.cm.hot)
return fig,
def show_frame(i):
ax.view_init(30., i)
return fig,
# for Animation
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(
fig,
show_frame,
init_func=init,
frames=360,
interval=60,
blit=True,
)
# for save
mpl.rcParams['animation.embed_limit'] = 120
anim.save('3dplot.gif', fps=30)
# for jupyter notebook
from IPython.display import HTML
HTML(anim.to_jshtml())
4. Labels and Ticks
Axes3D 객체에서 ticks와 ticklabels 를 일반적인 Axes 객체와 마찬가지로 설정가능함.
set_xlabel: x축에 대한 label (str)set_ylabel: y축에 대한 labelset_zlabel: z축에 대한 label
ax.set_xlabel(r'$x', fonsize=10)
회전의 예제 코드는 다음과 같음.
set_xticks: x축에 대한 ticks 위치. listset_yticks: y축에 대한 ticks 위치.set_zticks: z축에 대한 ticks 위치.
ax.set_xticks([-10, -5, 0, 5, 10])set_xticklabels: x축의 tick 밑의 label. listset_yticklabels: y축의 tick 밑의 label.set_zticklabels: z축의 tick 밑의 label.
ax.set_xticklabels([r'$-2\pi$', r'-$\pi$', 0, r'$\pi$', r'$2\pi$'])'Python > matplotlib' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [matplotlib] pseudocolor plot: pcolor (1) | 2024.01.22 |
|---|---|
| [matplotlib] Layout Managers: GridSpec and subplot2grid (1) | 2024.01.22 |
| [matplotlib] x축과 y축을 그리기: spines (0) | 2023.08.08 |
| [matplotlib] line 및 marker 설정하기. (0) | 2023.07.21 |
| [matplotlib] : backend 란 (0) | 2023.07.20 |


